1024 rows by 1024 columns. Each location holds one byte. How many megabytes?
1024 × 1024 = 210 × 210 = 2(10+10) = 220 = one megabyte
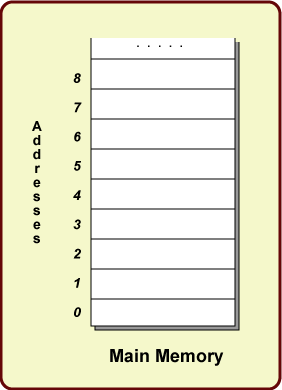
Main memory consists of a very long list of bytes. In most modern computers, each byte has an address that is used to locate it. The picture shows a small part of main memory:
Each box in this picture represents a single byte. Each byte has an address. In this picture the addresses are the integers to the left of the boxes: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, ... and so on. The addresses for most computer memory start at 0 and go up in sequence until each byte has an address.
Each byte contains a pattern of eight bits. When the computer's power is on, every byte contains some pattern or other, even when those bytes are not being used for anything. (Remember the nature of binary: when a binary device is working it is either "on" or "off", never in-between.)
The address of a byte is not explicitly contained in memory. When the processor needs to access the byte at a particular address, the electronics of the computer "knows how" to find that byte in memory.
Decide if the following are true: