Can an object contain a reference to another object?
Of course. We have seen this many times.
For example, an object frequently contains a reference to a String object.
Can an object contain a reference to another object of the same class as itself?
Sure.
Examine the following Java class:
// Node.java
//
public class Node
{
private int value;
private Node next;
// Constructor. Make a Node containing val.
// Initialize next to null
public Node ( int val )
{
value = val;
next = null;
}
public int getValue() { return value; } // get the value in this Node
public Node getNext() { return next; } // get a pointer to another Node
public void setValue( int val ) { value = val; }
public void setNext( Node nxt ) { next = nxt; }
public String toString() { return "" + value; } // return a string based on value
}
Recall that + means string concatenation.
String concatenation automatically uses the toString()
method of the object.
Here is a program that tests the class:
// NodeTester.java
//
public class NodeTester
{
public static void main ( String[] args )
{
Node node0 = new Node( 223 );
System.out.println("Node 0: " + node0 );
}
}
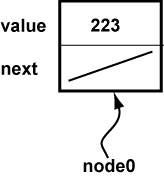
The program constructs a Node object and puts a reference to in in node0.
The member next is of type Node
(a potential reference to another Node object).
The slash in next represents the null put there by the constructor.
So to start, it points to no object.
Compile and run the program:
C:\JavaSource> javac Node.java NodeTester.java C:\JavaSource> java NodeTester Node 0: 223 C:\JavaSource>
What is the output of the following:
public class NodeTester
{
public static void main ( String[] args )
{
Node node0 = new Node( 223 );
System.out.println("Node 0: " + node0 );
node0.setValue( 17 );
System.out.println("new value: " + node0 );
}
}